概述
Wireshark可以捕获网络数据包,并显示数据包的信息。但是需要注意的是,它只能查看数据包的内容,但是不能修改其内容,也不能发送数据包。
Wireshark抓包的原理是捕获机器上的某一块网卡的网络包,当机器上有多块网卡的时候,需要选择一个网卡。
基本操作
在启动时,Wireshark会弹出一个选择网卡的界面:
双击选择要抓包的网卡,然后数据包采集的过程便会自动开始。抓包的界面如下。为保护隐私,隐去了一部分敏感信息。
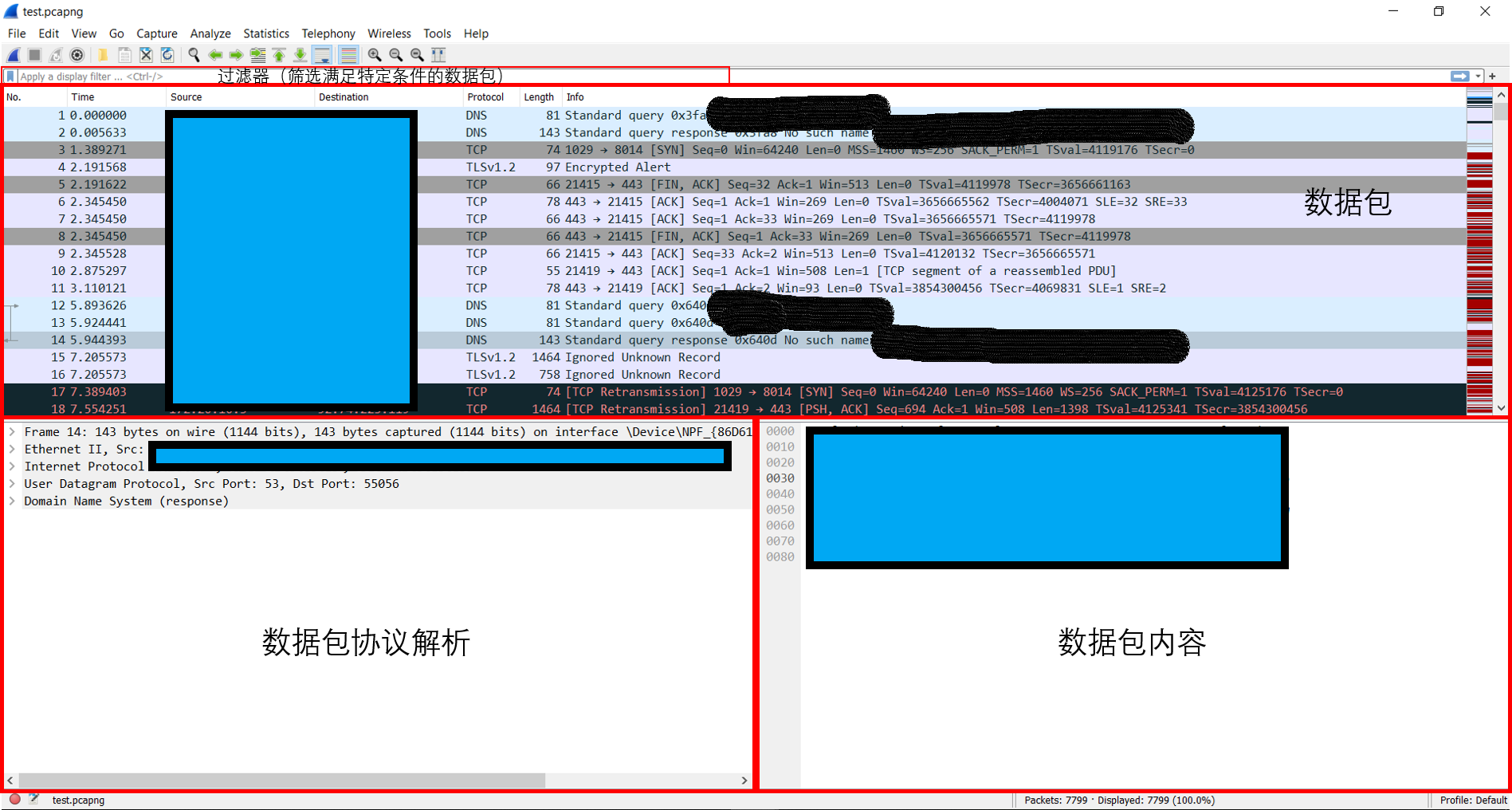
我们可以看到,对于每个数据包,Wireshark都会自动将它们按照物理层、数据链路层、网络层、传输层和应用层的顺序进行解析。点开之后可以查看数据包每一层报文的表头及其内容,但是如果为TLS加密后的数据包,在经过解析之后只能看到被加密的内容,无法还原出原始数据。
实例1:访问网页
我们以访问www.github.com为例,抓取并分析这一过程中产生的数据包。其大致过程如下:
由于抓包的时候计算机可能会有各种不同的网络活动,因此在我们用浏览器访问www.github.com的这一过程中,同时也会抓取到与之无关的一些数据包。所以我们在过滤器一栏中输入DNS,先根据DNS协议进行筛选,找到www.github.com对应的ip地址:
从中可以看到,DNS协议找到了www.github.com对应的ip地址为13.229.188.59。从DNS协议的数据包中我们也可以看到,它使用的是UDP协议(计算机网络的基础知识)
接下来,我们筛选包含这一ip地址的数据包,在过滤器一栏中输入ip.addr == 13.229.188.59,便可过滤出访问www.github.com相关的数据包。但是发现此时有两个不同的端口(本例为1038和1046)都与www.github.com建立了HTTPS连接(不知道是否为个例),所以我们再对端口进行过滤,方便分析,过滤语句为:ip.addr == 13.229.188.59 and tcp.port eq 1038
此时便可以看到三次握手的过程(其中Seq和Ack字段为相对值,其原本的值是一个随机数):
TCP 74 1038 → 443 [SYN] Seq=0 Win=64240 Len=0 MSS=1460 WS=256 SACK_PERM=1 TSval=4126304 TSecr=0
TCP 74 443 → 1038 [SYN, ACK] Seq=0 Ack=1 Win=65535 Len=0 MSS=1410 SACK_PERM=1 TSval=2421957921 TSecr=4126304 WS=1024
TCP 66 1038 → 443 [ACK] Seq=1 Ack=1 Win=131328 Len=0 TSval=4126734 TSecr=2421957921
因为建立HTTPS连接,也可以看到TLS协议交换证书、协商密钥并建立安全连接的过程:
TLSv1.2 259 Client Hello
TLSv1.2 1464 Server Hello
TCP 1464 443 → 1038 [ACK] Seq=1399 Ack=194 Win=67584 Len=1398 TSval=2421958344 TSecr=4126734 [TCP segment of a reassembled PDU]
TLSv1.2 677 Certificate, Server Key Exchange, Server Hello Done
TCP 66 1038 → 443 [ACK] Seq=194 Ack=3408 Win=131328 Len=0 TSval=4127177 TSecr=2421958344
TLSv1.2 159 Client Key Exchange, Change Cipher Spec, Encrypted Handshake Message
TCP 1464 1038 → 443 [ACK] Seq=287 Ack=3408 Win=131328 Len=1398 TSval=4127178 TSecr=2421958344 [TCP segment of a reassembled PDU]
TLSv1.2 758 Application Data
TLSv1.2 117 Change Cipher Spec, Encrypted Handshake Message
TCP 66 1038 → 443 [ACK] Seq=2377 Ack=3459 Win=131328 Len=0 TSval=4127664 TSecr=2421958801
之后,可以看到服务器端主动断开了连接:
TCP 97 [TCP Retransmission] 443 → 1038 [FIN, PSH, ACK] Seq=50533 Ack=19038 Win=117760 Len=31 TSval=2422185452 TSecr=4353563 TCP 66 1038 → 443 [FIN, ACK] Seq=19069 Ack=50565 Win=130304 Len=0 TSval=4354286 TSecr=2422185452
实例2:ping命令
在command框里面输入www.baidu.com,Wireshark中便会抓取到相关的信息。ping命令使用的是ICMP协议:
ICMP 74 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=2/512, ttl=128 (reply in 61) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) reply id=0x0001, seq=2/512, ttl=53 (request in 60) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=3/768, ttl=128 (reply in 64) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) reply id=0x0001, seq=3/768, ttl=53 (request in 63) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=4/1024, ttl=128 (reply in 71) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) reply id=0x0001, seq=4/1024, ttl=53 (request in 70) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=5/1280, ttl=128 (reply in 73) ICMP 74 Echo (ping) reply id=0x0001, seq=5/1280, ttl=53 (request in 72)
实例3:tracert命令
C:>tracert www.baidu.com
Tracing route to www.a.shifen.com [112.80.248.75] over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 11 ms 1 ms 1 ms [*] 2 * * * Request timed out. 3 84 ms 303 ms 34 ms [10.215.12.209] 4 * * * Request timed out. 5 * * * Request timed out. 6 271 ms 35 ms 20 ms 58.247.221.25 7 * * 68 ms 139.226.214.38 8 43 ms 49 ms 19 ms 139.226.210.85 9 51 ms 39 ms 28 ms 219.158.97.106 10 86 ms 38 ms 27 ms 221.6.1.254 11 102 ms 55 ms 35 ms 58.240.60.166 12 * * * Request timed out. 13 93 ms 42 ms 123 ms 112.80.248.75
Trace complete.
在这一过程中,我们可以看到有ARP协议的数据包(为保护隐私略去了MAC地址和ip地址),去请求与自己直接相连的路由器的MAC地址:
ARP 42 Who has 172.*? Tell 172.* ARP 42 172.* is at *(MAC address)
我们使用目的地址112.80.248.75进行过滤,可以得到一系列的ICMP ping请求数据包:
ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=75/19200, ttl=1 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=76/19456, ttl=1 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=77/19712, ttl=1 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=78/19968, ttl=2 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=79/20224, ttl=2 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=80/20480, ttl=2 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=81/20736, ttl=3 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=82/20992, ttl=3 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=83/21248, ttl=3 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=84/21504, ttl=4 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=85/21760, ttl=4 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=86/22016, ttl=4 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=87/22272, ttl=5 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=88/22528, ttl=5 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=89/22784, ttl=5 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=90/23040, ttl=6 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=91/23296, ttl=6 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=92/23552, ttl=6 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=93/23808, ttl=7 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=94/24064, ttl=7 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=95/24320, ttl=7 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=96/24576, ttl=8 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=97/24832, ttl=8 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=98/25088, ttl=8 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=99/25344, ttl=9 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=100/25600, ttl=9 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=101/25856, ttl=9 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=102/26112, ttl=10 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=103/26368, ttl=10 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=104/26624, ttl=10 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=105/26880, ttl=11 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=106/27136, ttl=11 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=107/27392, ttl=11 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=108/27648, ttl=12 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=109/27904, ttl=12 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=110/28160, ttl=12 (no response found!) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=111/28416, ttl=13 (reply in 303) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=112/28672, ttl=13 (reply in 305) ICMP 106 Echo (ping) request id=0x0001, seq=113/28928, ttl=13 (reply in 307)
从中我们可以发现,这些ICMP数据包的ttl值在一直递增,这也正好符合tracert的工作原理。
同时,我们也能收到一系列的ICMP响应数据包,只有来自于112.80.248.75的数据包内容为ping响应,来自其它中间地址的数据包,例如10.215.12.209,则内容全部为:
ICMP 70 Time-to-live exceeded (Time to live exceeded in transit)
附:tracert工作原理
tracert 命令用 IP 生存时间 (TTL) 字段和 ICMP 错误消息来确定从一个主机到网络上其他主机的路由。
首先,tracert送出一个TTL是1的ICMP ping请求数据包到目的地,当路径上的第一个路由器收到这个数据包时,它将TTL减1。此时,TTL变为0,所以该路由器会将此数据包丢掉,并送回一个「ICMP time exceeded」消息(包括发IP包的源地址,IP包的所有内容及路由器的IP地址),tracert 收到这个消息后,便知道这个路由器存在于这个路径上,接着tracert 再送出另一个TTL是2 的数据包,发现第2 个路由器...... tracert 每次将送出的数据包的TTL 加1来发现另一个路由器,这个重复的动作一直持续到某个数据包 抵达目的地。当数据包到达目的地后,该主机则可以响应ICMP ping请求,并发送ICMP ping响应。
tracert 有一个固定的时间等待响应(ICMP TTL到期消息)。如果这个时间过了,它将打印出一系列的*号表明:在这个路径上,这个设备不能在给定的时间内发出ICMP TTL到期消息的响应。然后,tracert给TTL记数器加1,继续进行。
参考
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30135181/article/details/50992151
- https://www.cnblogs.com/mq0036/p/11187138.html

